Cybersecurity Failures: Direct and Indirect Costs and their Primary Causes
Downtime costs large companies hundreds of billions annually, with significant financial and reputational impacts. Understanding and mitigating these costs is crucial for business continuity and competitiveness. The recent Splunk report shows that strong cybersecurity measures, observability practices, and IT-security convergence are important in order to reduce cybersecurity failures and thus mitigate the risk of downtime. Insights from industry analyses also support this idea that cybersecurity can be a detriment if certain actions are not taken.

Key Findings from the Splunk Report
- Direct Financial Impact:
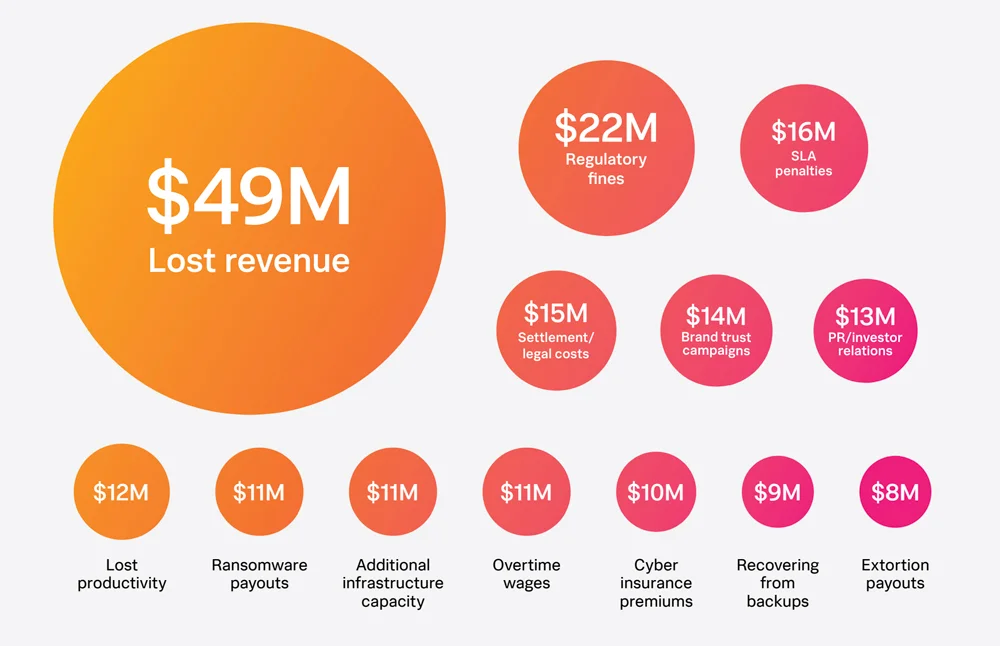
- Lost Revenue: The primary financial loss, averaging $49 million per company annually.
- Regulatory Fines: Approximately $22 million due to compliance failures.
- Reputation Management: Around $14 million for brand restoration and $13 million for public relations efforts.
2. Hidden Costs:
- Shareholder Value: A 2.5% drop in stock price, taking about 79 days to recover.
- Operational Delays: Reduced time-to-market and innovation stagnation.
- Customer Loyalty: A significant loss in customer lifetime value due to negative experiences.
3. Primary Causes:
- Human Errors: Cybersecurity-related mistakes such as phishing attacks.
- IT Operations: Misconfigurations and capacity issues.
- Software Failures and Malware: Increasing risks with complex systems.
Broader Industry Context Comparison
1. Financial Impact:
- Splunk Report: Downtime costs an average of $365,000 per hour, with large companies facing annual losses of around $400 billion due to unscheduled outages (Datanami).
- Industry Insights: ITIC’s research found that 91% of mid-to-large enterprises report downtime costs exceeding $300,000 per hour, with some reaching over $1 million (Trilio). The costs are particularly high in sectors like banking, healthcare, and manufacturing.
2. Causes and Frequency:
- Cyberattacks: Increasing in frequency and sophistication, cyberattacks are a major cause of cybersecurity failures leading to downtime. The Splunk report notes that 52% of organizations experienced a data breach in the past two years, up from previous years (SiliconANGLE) (IT Security Demand).
- Complex Infrastructures: The adoption of cloud technologies and hybrid environments contributes to system failures and downtime, necessitating specialized cyber security data protection and disaster recovery solutions (Trilio).
3. Operational and Hidden Costs:
- Revenue Loss: Downtime leads to significant revenue loss, with average costs per company reaching $49 million annually (Datanami).
- Reputational Damage: Downtime affects customer trust and shareholder value, with a noted 2.5% drop in stock prices taking about 79 days to recover (SiliconANGLE).
- Innovation Delays: Frequent downtimes delay product launches and reduce overall market competitiveness (IT Security Demand).

Solutions and Best Practices
1. Investing in Cybersecurity:
- Companies are increasingly allocating larger budgets to cybersecurity, with a focus on improving detection, data capture, and analysis to prevent and mitigate the impact of attacks (IT Security Demand).
2. Enhancing Observability:
- Mature observability practices are crucial for quickly identifying and resolving issues, thereby reducing downtime. This involves using tools that provide real-time insights into system performance and security (Datanami).
- Postmortems and Continuous Improvement: Regular analysis of downtime incidents to prevent recurrence.
- Data Governance: Establishing clear policies to protect sensitive information.
3. Convergence of IT and Security Operations:
- Integrating IT and security operations improves risk visibility and response coordination. This collaborative approach helps in addressing vulnerabilities more effectively and ensuring business continuity during incidents (SiliconANGLE) (IT Security Demand).
4. Service Level Agreements (SLAs):
- Establishing clear SLAs helps manage expectations, define acceptable levels of service disruption, and outline penalties for breaches. This framework ensures accountability and minimizes the financial and reputational risks associated with downtime (Trilio).
Expert Insights and Engagement
Consulting with cybersecurity experts and incorporating their insights ensures that the analysis remains practical and actionable. Engaging storytelling and real-world examples can make the content more relatable and interesting, thereby enhancing reader engagement and comprehension.
Practical Approaches Practices
- Resilience Strategies:
- Security Investments: Top resilience leaders invest significantly in security tools and infrastructure.
- AI and Predictive Analytics: Leveraging AI to anticipate and mitigate downtime.
2. Operational Improvements:
- Postmortems and Continuous Improvement: Regular analysis of downtime incidents to prevent recurrence.
- Data Governance: Establishing clear policies to protect sensitive information.
3. Crisis Management:
- Downtime Plans: Detailed runbooks and incident response drills.
- Cross-Department Collaboration: Ensuring seamless communication and cooperation during incidents.
Conclusion
Downtime presents a significant risk to business operations, with substantial financial and reputational costs. The insights provided by the Splunk report align closely with broader industry data and expert analysis. The financial and operational impacts of downtime are well-documented across multiple sources, reinforcing the report’s credibility that cybersecurity failures are a top issue for business risks.
By understanding the underlying causes and implementing comprehensive resilience strategies — such as enhanced cybersecurity measures, robust observability practices, and IT-security convergence — companies can effectively mitigate these risks and ensure operational continuity.
For further reading and detailed insights, access the full Splunk report and related analyses through their official publications and industry reviews on platforms like TechRepublic, SiliconANGLE, and ITSecurity Demand (Datanami) (SiliconANGLE) (IT Security Demand).
Note: (originally released here on 14 Jun 24 titled: Unveiling the True Cost of Downtime: How Cybersecurity Failures Can Cripple Your Business — $400 Billion a Year!





